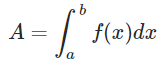NCERT Maths Formulas are created by expert teachers from the latest edition books. Basic Maths formulas enable students to complete the syllabus in a unique do-learn-do pattern of study. These mathematical formulas help students:
- Improve Score in Board Exams and Entrance Examinations.
- Makes Complete Preparation easy on time.
- Helps you in making revision
- Mind Maps and Tables Helps you to Memories easily.
- Know their strengths and weaknesses in Mathematics formula
- NCERT Math Formulas are indispensable for students preparing for competitive Exams and Board Exams.
- Math formula empowers students for hands-on practice and helps them to score high on both in-class exams and boards.
NCERT Maths Formulas | Class 6 to Class 12
Important NCERT Maths Formulas | Area Formulas
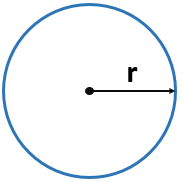
- Area of a Circle Formula = π r2
where
r – radius of a circle

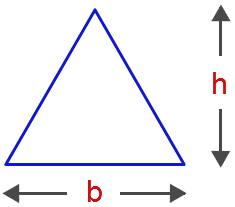
- Area of a Triangle Formula A=( frac{1}{2} b h )
where
b – base of a triangle.
h – height of a triangle.

- Area of Equilateral Triangle Formula = ( frac{sqrt{3}}{4} s^{2} )
where
s is the length of any side of the triangle.

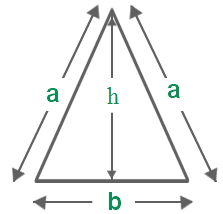
- Area of Isosceles Triangle Formula = ( frac{1}{2} b h )

where:
a be the measure of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle.
b be the base of the isosceles triangle.
h be the altitude of the isosceles triangle. - Area of a Square Formula = a2

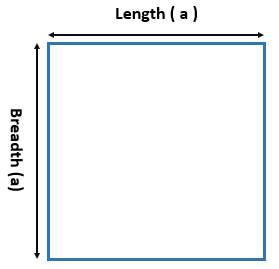
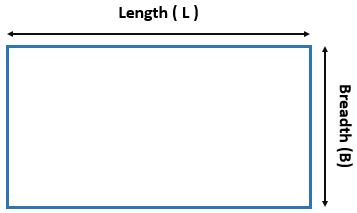
- Area of a Rectangle Formula = L. B
where
L is the length.
B is the Breadth.
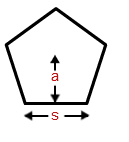
- Area of a Pentagon Formula = ( frac{5}{2} s . a )
Where
s is the side of the pentagon.
a is the apothem length.

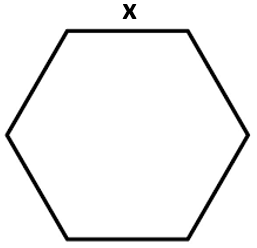
- Area of a Hexagon Formula = (frac{3 sqrt{3}}{2} x^{2} )
where
where “x” denotes the sides of the hexagon.

Area of a Hexagon Formula = (frac{3}{2} . d . t )
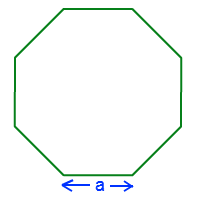
Where “t” is the length of each side of the hexagon and “d” is the height of the hexagon when it is made to lie on one of its bases of. - Area of an Octagon Formula = ( 2 a^{2}(1+sqrt{2}) )
Consider a regular octagon with each side “a” units.

- Area of Regular Polygon Formula:
By definition, all sides of a regular polygon are equal in length. If you know the length of one of the sides, the area is given by the formula:
 where
where
s is the length of any side
n is the number of sides
tan is the tangent function calculated in degrees

- Area of a Parallelogram Formula = b . a
where
b is the length of any base
a is the corresponding altitude Area of Parallelogram: The number of square units it takes to completely fill a parallelogram.
Area of Parallelogram: The number of square units it takes to completely fill a parallelogram.
Formula: Base × Altitude - Area of a Rhombus Formula = b . a
where
b is the length of the base
a is the altitude (height).

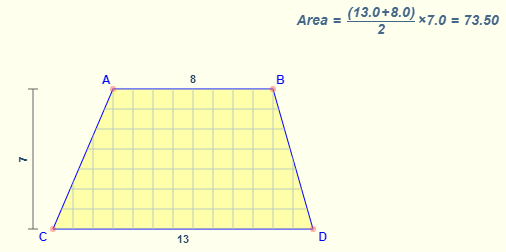
- Area of a Trapezoid Formula = The number of square units it takes to completely fill a trapezoid.
Formula: Average width × Altitude

The area of a trapezoid is given by the formula
 where
where
b1, b2 are the lengths of each base
h is the altitude (height)

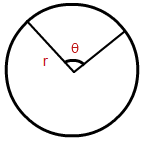
- Area of a Sector Formula (or) Area of a Sector of a Circle Formula = (pi r^{2}left(frac{C}{360}right) )
where:
C is the central angle in degrees
r is the radius of the circle of which the sector is part.
π is Pi, approximately 3.142
 Sector Area – The number of square units it takes to exactly fill a sector of a circle.
Sector Area – The number of square units it takes to exactly fill a sector of a circle. - Area of a Segment of a Circle Formula
Area of a Segment in Radians (A =1 / 2 times r^{2}(theta-sin theta) )
Area of a Segment in Degrees (A =frac{1}{2} r^{2}left(frac{pi}{180} theta-sin thetaright) )
 Area of a Segment of a Circle Formula
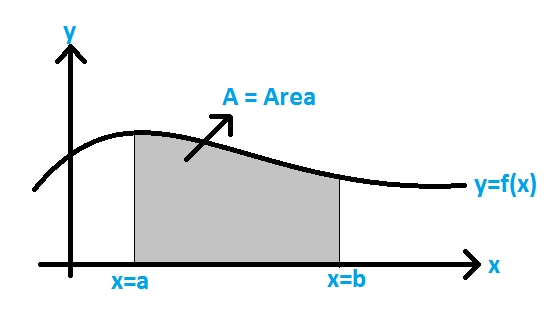
Area of a Segment of a Circle Formula - Area under the Curve Formula:
The area under a curve between two points is found out by doing a definite integral between the two points. To find the area under the curve y = f(x) between x = a & x = b, integrate y = f(x) between the limits of a and b. This area can be calculated using integration with given limits.


- Area of a Circle Formula = π r2
Algebra Formulas | NCERT Maths Formulas
1. (a^{2}-b^{2}=(a+b)(a-b)) [mathjax]
2. ((a+b)^{2}=a^{2}+2 a b+b^{2})
3. (a^{2}+b^{2}=(a-b)^{2}+2 a b)
4. ((a-b)^{2}=a^{2}-2 a b+b^{2})
5. ((a+b+c)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+2 a b+2 a c+2 b c)
6. ((a-b-c)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}-2 a b-2 a c+2 b c)
7. ((a+b)^{3}=a^{3}+3 a^{2} b+3 a b^{2}+b^{3} ;(a+b)^{3}=a^{3}+b^{3}+3 a b(a+b))
8. ((a-b)^{3}=a^{3}-3 a^{2} b+3 a b^{2}-b^{3})
9. (a^{3}-b^{3}=(a-b)left(a^{2}+a b+b^{2}right))
10. (a^{3}+b^{3}=(a+b)left(a^{2}-a b+b^{2}right))
11. ((a+b)^{4}=a^{4}+4 a^{3} b+6 a^{2} b^{2}+4 a b^{3}+b^{4})
12. ((a-b)^{4}=a^{4}-4 a^{3} b+6 a^{2} b^{2}-4 a b^{3}+b^{4})
13. (a^{4}-b^{4}=(a-b)(a+b)left(a^{2}+b^{2}right))
14. (a^{5}-b^{5}=(a-b)left(a^{4}+a^{3} b+a^{2} b^{2}+a b^{3}+b^{4}right))
15. ((x+y+z)^{2}=x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}+2 x y+2 y z+2 x z)
16. ((x+y-z)^{2}=x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}+2 x y-2 y z-2 x z)
17. ((x-y+z)^{2}=x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}-2 x y-2 y z+2 x z)
18. ((x-y-z)^{2}=x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}-2 x y+2 y z-2 x z)
19. (x^{3}+y^{3}+z^{3}-3 x y z=(x+y+z)left(x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}-x y-y z-x zright))
20. (x^{2}+y^{2}=frac{1}{2}left[(x+y)^{2}+(x-y)^{2}right])
21. ((x+a)(x+b)(x+c)=x^{3}+(a+b+c) x^{2}+(a b+b c+c a) x+a b c)
22. (x^{3}+y^{3}=(x+y)left(x^{2}-x y+y^{2}right))
23. (x^{3}-y^{3}=(x-y)left(x^{2}+x y+y^{2}right))
24. (x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}-x y-y z-z x=frac{1}{2}left[(x-y)^{2}+(y-z)^{2}+(z-x)^{2}right])
25. if n is a natural number, (a^{n}-b^{n}=(a-b)left(a^{n-1}+a^{n-2} b+ldots+b^{n-2} a+b^{n-1}right))
26. if n is even n = 2k, (a^{n}+b^{n}=(a+b)left(a^{n-1}-a^{n-2} b+ldots+b^{n-2} a-b^{n-1}right))
27. if n is odd n = 2k+1, (a^{n}+b^{n}=(a+b)left(a^{n-1}-a^{n-2} b+ldots-b^{n-2} a+b^{n-1}right))
28. ((a+b+c+ldots)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+ldots+2(a b+b c+ldots))
29. (begin{aligned}left(a^{m}right)left(a^{n}right) &=a^{m+n} \(a b)^{m} &=a^{m} b^{m} \left(a^{m}right)^{n} &=a^{m n} end{aligned})
30. (begin{aligned} a^{0} &=1 \ frac{a^{m}}{a^{n}} &=a^{m-n} \ a^{m} &=frac{1}{a^{-m}} \ a^{-m} &=frac{1}{a^{m}} end{aligned})
Root Maths Formulas
Square Root :
If x2 = y then we say that square root of y is x and we write √y = x
So, √4 = 2, √9 = 3, √36 = 6
Cube Root:
The cube root of a given number x is the number whose cube is x.
we can say the cube root of x by 3√x
- √xy = √x * √y
- √x/y = √x / √y = √x / √y x √y / √y = √xy / y.
Fractions Maths Formulas
What is a fraction?
Fraction is the name of part of a whole.
Let the fraction number is 1 / 8.
Numerator: Number of parts that you of the top number(1)
Denominator: It is the number of equal parts the whole is divided into the bottom number (8).
We hope the Maths Formulas for Class 6 to Class 12, help you. If you have any queries regarding Class 6 to Class 12 Maths Formulas, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
FAQs on NCERT Maths Formulas
1. What is the best way to memorize Math Formulas?
The best way to remember math formulas to learn how to derive them. If you can derive them then there is no need to remember them.
2. How to learn Mathematics Formulas?
Don’t try to learn the formula try learning the logic behind the formula and intuition behind it.
3. What is Math Formula?
Generally, each kind of maths has a formula or multiple formulas that help you work out a particular thing, whether it’s geometry, statistics, measurements, etc.
4. Is it necessary to know how does a math formula work?
It is indeed necessary to understand and be able to solve equations, either if you want to work as a mathematician, or any other field using mathematics, or if you want to be a math teacher or a teacher in a field that uses math.
Also Read: Cowin App registration login for 18+ citizens process (1st 2nd dose)
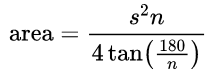 where
where
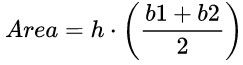 where
where
 Sector Area – The number of square units it takes to exactly fill a sector of a circle.
Sector Area – The number of square units it takes to exactly fill a sector of a circle.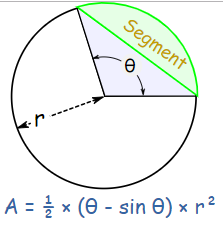 Area of a Segment of a Circle Formula
Area of a Segment of a Circle Formula